42 goto and labels in c
goto statement in C - tutorialspoint.com The syntax for a goto statement in C is as follows − goto label; .. . label: statement; Here label can be any plain text except C keyword and it can be set anywhere in the C program above or below to goto statement. Flow Diagram Example Live Demo goto - Arduino Reference The use of goto is discouraged in C programming, and some authors of C programming books claim that the goto statement is never necessary, but used judiciously, it can simplify certain programs. The reason that many programmers frown upon the use of goto is that with the unrestrained use of goto statements, it is easy to create a program with undefined program flow, which can never be debugged.
goto statement in C - Codeforwin Syntax of goto statement label: goto label; Parts of goto statement. goto is divided in two parts, label definition and goto keyword. Label is a valid C identifier followed by colon symbol :. Label specifies control transfer location. Each label work as a bookmark to specific location. You are free to define any number of labels anywhere inside ...

Goto and labels in c
goto and Labeled Statements (C) | Microsoft Docs The goto statement transfers control to a label. The given label must reside in the same function and can appear before only one statement in the same function. Syntax statement: labeled-statement jump-statement jump-statement: goto identifier ; labeled-statement: identifier : statement c++ - How to store goto labels in an array and then jump to them ... There's no direct way to store code addresses to jump to in C. How about using switch. #define jump (x) do { label=x; goto jump_target; }while (0) int label=START; jump_target: switch (label) { case START: /* ... */ case LABEL_A: /* ... */ } You can find similar code produced by every stack-less parser / state machine generator. Use the goto Statement in C | Delft Stack Any statement in code can be preceded by a label, which is just an identifier followed by a colon. goto call forces the code execution to jump to the first statement after the label. goto can only jump to the label inside the same function and labels are visible in the entire function regardless on which line they are defined.
Goto and labels in c. C# Goto Statement The goto statement is a jump statement that controls the execution of the program to another segment of the same program. You create a label at anywhere in the program then can pass the execution control via the goto statements. Example: using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace goto_statements Discover Goto and Labels in C++ goto mylabel; to use this, we must also define mylabel there. label is an identifier that identifies a labeled line or statement and a labeled statement is a statement that is preceded by an identifier followed by a colon ':' character, labels are alpahnumeric texts without spaces, for example we can define mylabel like this, 1 2 3 4 mylabel: Goto Statement in C - HashCodec goto is a jumping statement in c language, which transfers the program's control from one statement to another statement (where the label is defined). When the compiler reaches the goto statement, then it will jump unconditionally (both forward and backward) to the location specified in the goto statement (we called it a label). goto statement in C language - ssonline coding The goto statement is used to alter the normal sequence program execution by unconditionally transferring control to some other part of the program. This statement is written as. Here label is an identifier used to label the target statement to which the control would be transferred Control may be transferred to any other statement within the ...
goto Statement in C with Example - Know Program The control is unconditionally transferred to the statement associated with the label specified in the goto statement. goto syntax in C. Syntax:- goto label_name; A statement label is defined in exactly the same way as a variable name, which is a sequence of letters and digits, the first of which must be a letter. C++ goto statement - tutorialspoint.com The syntax of a goto statement in C++ is − goto label; .. . label: statement; Where label is an identifier that identifies a labeled statement. A labeled statement is any statement that is preceded by an identifier followed by a colon (:). Flow Diagram Example Live Demo goto statement in C/C++ - GeeksforGeeks In the above syntax, the first line tells the compiler to go to or jump to the statement marked as a label. Here label is a user-defined identifier which indicates the target statement. The statement immediately followed after 'label:' is the destination statement. The 'label:' can also appear before the 'goto label;' statement in the above syntax. goto Statement (C++) | Microsoft Docs The goto statement unconditionally transfers control to the statement labeled by the specified identifier. Syntax Copy goto identifier; Remarks The labeled statement designated by identifier must be in the current function. All identifier names are members of an internal namespace and therefore do not interfere with other identifiers.
'goto' Statement in C language - Includehelp.com goto is a jumping statement in c language, which transfer the program's control from one statement to another statement (where label is defined).. goto can transfer the program's within the same block and there must a label, where you want to transfer program's control.. Defining a label . Label is defined following by the given syntax. label_name: ... How does goto Statement Work in C++? - EDUCBA label: . . . goto label; This syntax 2 also works in a similar way as syntax one with a minute difference of structure following and manipulation. The goal is to find the target and perform a jump between the codes. Flowchart of goto Statement in C++. The flowchart of the goto statement in C++ with an explanation is given below. Use of goto statement in C programming - Aticleworld According to C standard, "A goto statement shall not jump from outside the scope of an identifier having a variably modified type to inside the scope of that identifier ". Example 1, #include int main(void) { int n = 9; goto Label; { int a[n]; Label: printf("Hello aticleworld\n"); } return 0; } Output: Example 2, #include C goto statement (with examples) - Algbly The label is an identifier. When goto label; is encountered, the control of program jumps to label: and executes the code below it. Note : We can use label anywhere in that function where the goto statement is used. goto statement Flowchart Syntax1 | Syntax2 ---------------------------- goto label; | label: . | . . | . . | . label: | goto label;
C# goto (With Examples) - Programiz In C#, we can use goto to break out of a for loop. For example, using System; namespace CSharpGoto { class Program { static void Main() { for(int i = 0; i <= 10; i++) { if(i == 5) { // transfers control to End label goto End; } Console.WriteLine (i); } // End label End: Console.WriteLine ("Loop End"); Console.ReadLine (); } } } Output
Local Labels in C - GeeksforGeeks Everybody who has programmed in C programming language must be aware about "goto" and "labels" used in C to jump within a C function. GCC provides an extension to C called "local labels". Conventional Labels vs Local Labels Conventional labels in C have function scope. Where as local label can be scoped to a inner nested block.
Will a label be executed if it is written before a goto statement in C? Answer (1 of 4): Labels aren't ever executed. They label stuff. But you can definitely have a label followed by a [code ]goto[/code] to it. For example if you didn ...
C goto Statement - W3schools C supports a unique form of a statement that is the goto Statement which is used to branch unconditionally within a program from one point to another. Although it is not a good habit to use the goto statement in C, there may be some situations where the use of the goto statement might be desirable. The goto statement is used by programmers to ...
C goto Statement - Programiz The goto statement allows us to transfer control of the program to the specified label. Syntax of goto Statement goto label; ... .. ... ... .. ... label: statement; The label is an identifier. When the goto statement is encountered, the control of the program jumps to label: and starts executing the code. Working of goto Statement
goto statement - cppreference.com Used when it is otherwise impossible to transfer control to the desired location using other statements. Syntax attr(optional) goto label ; Explanation The goto statement transfers control to the location specified by label. The goto statement must be in the same function as the label it is referring, it may appear before or after the label.
Goto Statement in C - Tutor Joe's The goto statement is a jump statement which is sometimes also referred to as unconditional jump statement. The goto statement can be used to jump from anywhere to anywhere within a function. Goto statement in C is a jump statement that is used to jump from one part of the code to any other part of the code in C. Syntax 1 : goto label ; . .
Goto and Labels in C - Tutorial And Example Goto Statement in C The goto statement is known as the jump statement in C. The goto is used to transfer the control of a program to a predefined label. C offers the infinitely-abusable goto statement, and labels to branch to. This means that the label is required as an identifier to a location where the branch is to be made.
C goto statement - javatpoint The goto statement is known as jump statement in C. As the name suggests, goto is used to transfer the program control to a predefined label. The goto statment can be used to repeat some part of the code for a particular condition. It can also be used to break the multiple loops which can't be done by using a single break statement.
Goto statement and labels in C - C Programming Simple Steps The goto statement in C The goto statement moves the execution of the program to another statement. The transfer of the control is unconditional and one-way. Syntax and rules The label : Must be defined within a function Each label in one function must have a unique name. It cannot be a reserved C word.
Goto Statement in C# with Examples - Dot Net Tutorials The goto statement transfers program control to a labeled statement. The label statement must exist in the scope of the goto statement. More than one goto statement can transfer control to the same label. This statement can be used to get out from a loop or an inner nested loop to an outer loop.
Use the goto Statement in C | Delft Stack Any statement in code can be preceded by a label, which is just an identifier followed by a colon. goto call forces the code execution to jump to the first statement after the label. goto can only jump to the label inside the same function and labels are visible in the entire function regardless on which line they are defined.
c++ - How to store goto labels in an array and then jump to them ... There's no direct way to store code addresses to jump to in C. How about using switch. #define jump (x) do { label=x; goto jump_target; }while (0) int label=START; jump_target: switch (label) { case START: /* ... */ case LABEL_A: /* ... */ } You can find similar code produced by every stack-less parser / state machine generator.
goto and Labeled Statements (C) | Microsoft Docs The goto statement transfers control to a label. The given label must reside in the same function and can appear before only one statement in the same function. Syntax statement: labeled-statement jump-statement jump-statement: goto identifier ; labeled-statement: identifier : statement









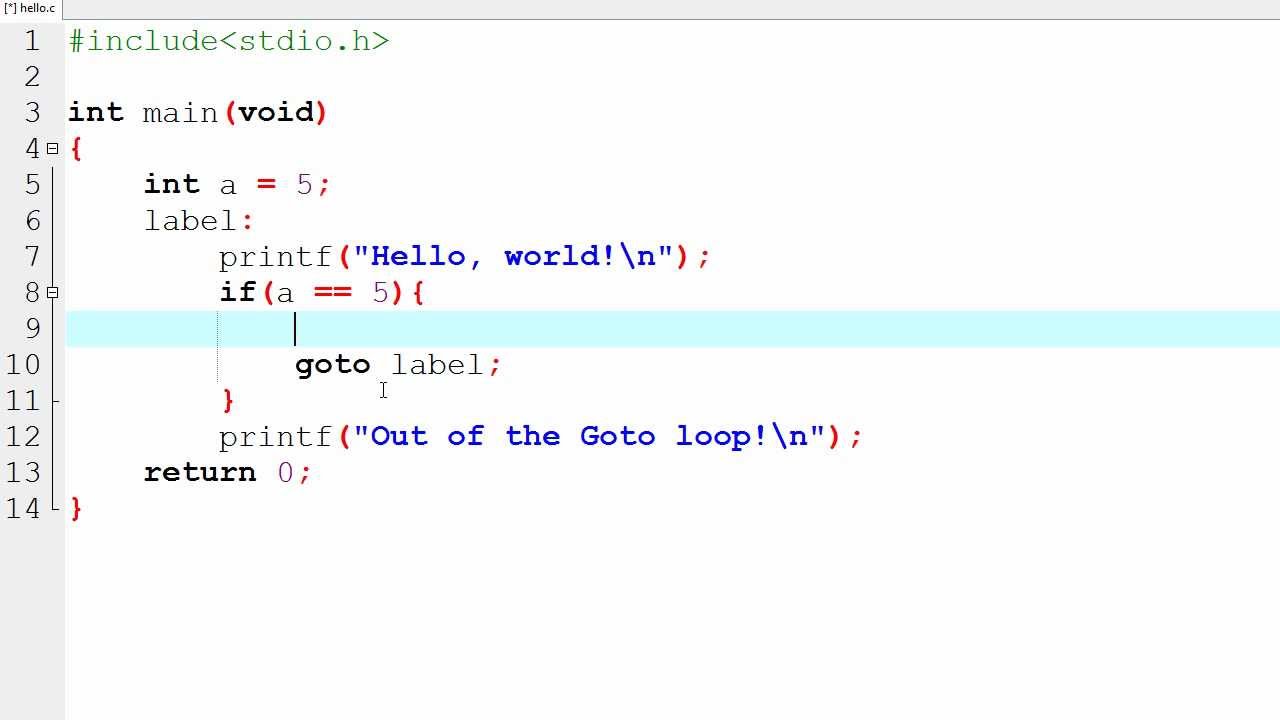



Post a Comment for "42 goto and labels in c"